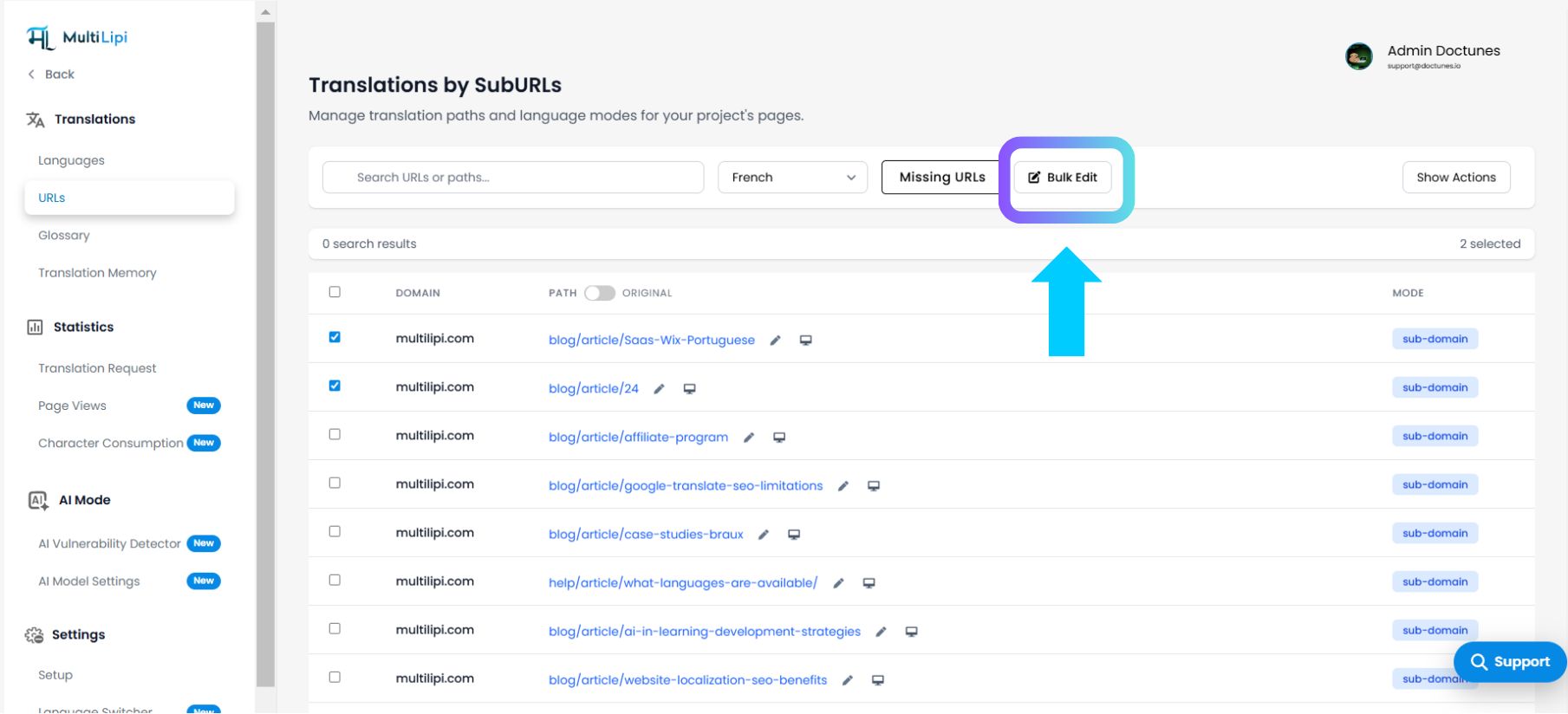
In large-scale web deployments, URL structures often change. You might decide to rename your entire /blog/ directory to /news/ across 500 translated pages. Doing this manually is operational suicide. MultiLipi's Bulk Slug Edit engine allows you to perform "Find & Replace" operations across your entire localized sitemap in seconds, ensuring your SEO strategy remains agile.
This guide details the protocol for executing these batch routing updates.
2. The Batch Protocol
Executing the Find & Replace logic.
Step 1: Selection Strategy
Manual Selection: Check the boxes beside specific URLs to target a subset (e.g., just the product pages).
Global Selection: You can choose to apply changes to the entire list in the next step.
Step 2: Initialize Operation
Klicken Sie auf das Symbol Bulk Editin der oberen rechten Ecke der Tabelle.
Systemaktion: This triggers the "Find & Replace" modal window.
Step 3: Define Pattern
Find: Enter the text string you want to remove (e.g., Artikel ).
Replace: Enter the new text string (e.g., articles).
Step 4: Define Scope
Choose the application scope:
Only selected items: Applies changes only to the rows you checked in Step 1.
All items: Applies the pattern match to every URL in the list (e.g., all 677 pages).
Step 5: Commit
Klicken Sie auf das Symbol Ersetzen Knopf.
Ergebnis: The engine processes the batch instantly. Your internal routing map is updated, and the new slugs go live immediately.
3. Strategic Use Cases
When to use batch operations.
Taxonomy Shifts: If your marketing team changes the category "Sweaters" to "Knitwear," you can update the slug for all 50 product pages in Spanish (/sueteres/ → /tejidos/) in one click.
Standardization: Fixing inconsistent naming conventions (e.g., ensuring all blog posts start with /blog- instead of just /).
Error Correction: Rapidly fixing a typo that propagated across multiple URLs during an AI translation batch.
4. Post-Deployment Protocol
Updating the search index.
Changing a URL (Slug) is a significant SEO event. After performing a bulk edit:
Regenerate Sitemap: Ensure your XML sitemap reflects the new paths.
Submit to Google: Log in to Google Search Console and resubmit your sitemap to force a re-crawl.
Redirects: If these pages were already indexed, ensure your underlying CMS handles 301 redirects from the old pattern to the new pattern to preserve traffic.